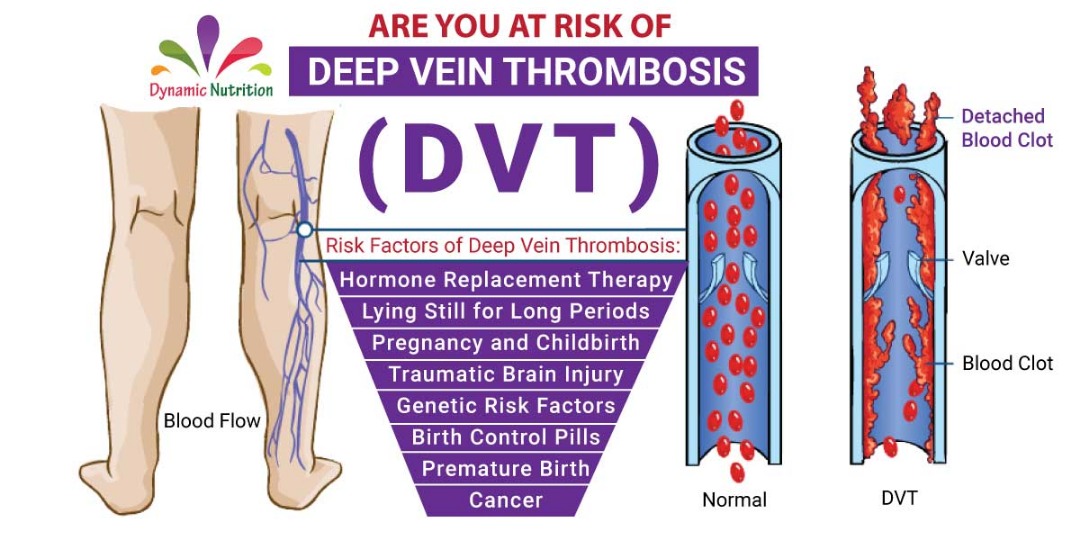
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in legs part. This can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur without any symptoms.
Deep vein thrombosis can develop if you have certain medical conditions that affect how your blood clots. It can also happen if you do not move for a long time, such as after surgery or an accident, or when you are confined to bed.
Furthermore, it can be very serious because blood clots in your veins can break loose. It travel through your bloodstream and lodge in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism).
Are you at Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Anyone can develop Deep Vein Thrombosis, but some people are at greater risk than others. Below are some risk factors of Deep Vein Thrombosis:
1. Premature Birth
If a baby born prematurely, before 37 weeks of pregnancy, will increase the risk for venous thromboembolism during infancy, childhood, and even young adulthood. The Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) reflects both Deep Vein Thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This serious condition happens when a blood clot breaks free, travels to a blood vessel feeding the lungs and lodges there.
2. Genetic Risk Factors
According to a research published in the British Journal of Haematology in 2013, about half of all participants who had a DVT had at least one genetic condition that affects how blood coagulates.
3. Pregnancy and Childbirth
A pregnant lady’s risk for Deep Vein Thrombosis increases substantially during pregnancy and again in the weeks of postpartum recovery.
4. Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills also increase the risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis. A woman’s specific risk depends on which formulation of the drug she is taking, age and obesity.
5. Cancer
Over the past 20 years, the blood clots of VTE have become the second leading cause of death among people with cancer.
6. Traumatic Brain Injury
People who sustain a traumatic brain injury may develop blood clots and Deep Vein Thrombosis. The clotting risk goes up when there are multiple injuries. For example, people who have both traumatic brain injury and injury to other parts of the body have an increased risk for clotting.
7. Hormone Replacement Therapy
Women and men alike stand to increase their risk if they take hormone replacement therapy. For women, hormone therapy that includes estrogen increases Deep Vein Thrombosis risk over time. While for men face an increase of DVT risk if they take testosterone replacement therapy.
8. Lying Still for Long Periods
Whether you are in the hospital or bedridden at home, the periods of immobility increase your risk for Deep Vein Thrombosis. However, researchers also found that people who were cared for a home had slightly less risk for Deep Vein Thrombosis.
Related Topics
7 Symptoms Of High Blood Pressure
COVID-19 increases risk of blood clots for up to six months
Side Effects Of Red Yeast Rice
Three Ways French Pine Bark Protects The Heart
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment With Nattokinase NSK-SD®
Are you at Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
New Guidelines Advise against Low-dose Aspirin to Prevent Strokes and Heart Attacks for Older Adults
How To Identify Signs Of Heart Attack
Top 5 Benefits Of Grape Seed Extract
The Risk Factors of High Blood Pressure and Simple Steps to Control it
Symptoms of Poor Blood Circulation











Facebook Comments