The liver is located on the upper-right side of the abdomen. It is the largest organ inside the body. The main functions of the liver are digest food, store energy, and remove poisons. Blood from the digestive system filters through the liver before traveling anywhere else in the body. If too much fat builds up in the liver, this can cause fatty liver.
What is Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver is a condition in which the cells of the liver accumulate abnormally increased amounts of fat. There are two main types of fatty liver:
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
-
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, also known as Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Excessive consumption of alcohol is a very common cause of fatty liver (alcoholic fatty liver). Another form of fatty liver is a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a manifestation of an abnormality of metabolism within the liver.
The liver is an important organ in the metabolism of fat. In nonalcoholic fatty liver, the handling of fat by liver cells is disturbed. When the rate of fat intake is much higher than the rate of the fats being disposed, fat accumulates in the liver.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver
The nonalcoholic fatty liver is classified as either fatty liver or steatohepatitis (NASH). Fatty liver is which you have fat in the liver but no inflammation or liver cell damage. NASH is you have fat, inflammation and liver cell damage. Inflammation and liver cell damage can cause fibrosis or scarring of the liver. Furthermore, it may even lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
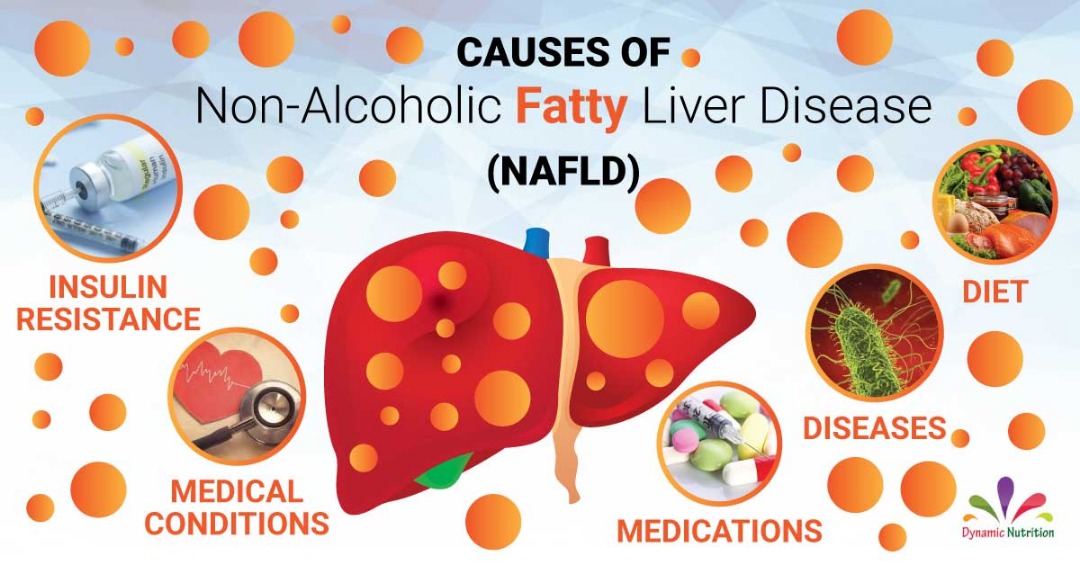
Causes of Fatty Liver (Nonalcoholic and Steatohepatitis)
There are many potential causes to fat accumulation in the liver:
1. Diet
Consumption of excess calories in the diet
2. Diseases
Fatty liver is also correlative with type II diabetes, obesity and high triglyceride levels in the blood, celiac disease and Wilson’s disease (abnormality of copper metabolism).
3. Medical conditions
Rapid weight loss and malnutrition
4. Medications
Medications such as tamoxifen (Soltamax), amiodarone injection (Nestorone), amiodarone oral (Cordarone, Pacerone), and methotrexate (Rheumatrex Dose Pack, Trexall) are associated with NAFLD.
5. Insulin Resistance
There is evidence to suggest the presence of an association between insulin resistance and the development of NAFLD. Although the body makes adequate insulin, the ability of cells to adequately use that insulin to metabolize glucose is abnormal. The relative excess of glucose is then stored as fat and can accumulate in the liver.
Significance of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver
Recognizing nonalcoholic fatty liver is important for a few reasons:
- The nonalcoholic fatty liver is a common disease and is increasing in prevalence.
- Steatohepatitis (NASH) is an important cause of serious liver disease, leading to cirrhosis and the complications of cirrhosis-liver failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, and liver cancer.
- The nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is correlative with other very common and serious non-liver diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases.








Facebook Comments