What is protein?
Protein is an essential nutrient involved in virtually all cell functions. In the body, protein is required for structural support, and the maintenance and repair of tissues. It is also the basic component for immunity, most hormones, and all enzymes, among other functions. In food, proteins are made from chains of 20 different amino acids, the building blocks of protein. Our bodies can only produce 11 of these amino acids. The 9 “essential” amino acids, which cannot be made by the body must be obtained from food. A diet with a variety of whole grains, legumes, and vegetables can provide all the essential amino acids to meet our bodies requirement.
How much protein do we need?
The recommended range of protein intake is between 0.8 g/kg and 1.8 g/kg of body weight, dependent on the many other factors. People who are highly active, or who wish to build more muscle should generally consume more protein. Some suggest consuming between 1.8 to 2 g/kg for those who are highly active. In short, the amount of protein you need daily based on your age, weight, height, lifestyle and fitness goals.
Calculate how much protein do you need daily with our protein calculator.

Why do vegetarian need more protein?
Vegetarians have higher protein requirements because plant proteins are not as well digested and processed by the body as animal proteins, and are not as ‘complete’ as protein from meat. So how much more is required?
It’s recommended that vegetarians eat 10% more protein than meat-eaters, and because vegans don’t eat eggs, milk or dairy products, they may need even more. Well-planned vegetarian eating patterns can offer a number of nutritional benefits over traditional meat containing diets. These include lower levels of saturated fat and higher levels of fiber, magnesium, potassium, folate and antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, and phytochemicals.
If you’re a vegetarian try to include soy, eggs and dairy products in your diet and you’ll find it easier to get the protein you need. For vegans, however, eating a variety of protein-containing foods daily (such as vegetables with nuts, rice with beans, or beans with corn) is essential to ensure an adequate protein intake. Inadequately-planned vegan and vegetarian diets may be low in vitamin B12, iron, calcium and zinc, as these nutrients are generally found in higher amounts in animal foods.
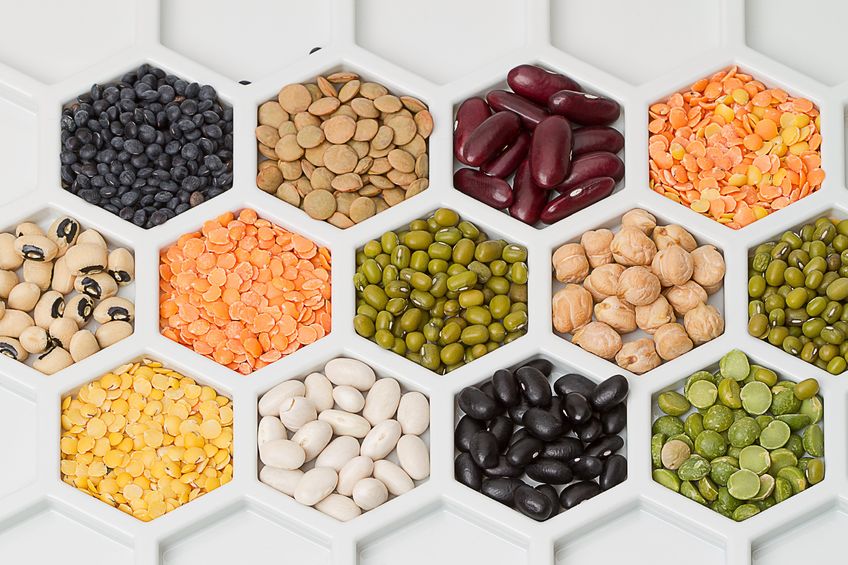
Plants That Are Rich In Protein
Plants are by nature rich sources of protein as they are made up of structural cells, hormones and enzymes. In fact, plants are so rich in protein that they meet the needs of the earth’s largest animals: elephants, giraffes, hippopotamuses, gorillas, cows, and horses. If these large animals with big, strong muscles can get adequate protein from plants, then so can we.
| FOOD | Amount | Protein (grams) |
|---|---|---|
| Tempeh | 1 cup | 41 |
| Seitan (seasoned wheat gluten) | 3 ounces | 31 |
| Soybeans, cooked | 1 cup | 29 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 1 cup | 25 |
| Lentils, cooked | 1 cup | 18 |
| Black beans, cooked | 1 cup | 15 |
| Kidney beans, cooked | 1 cup | 13 |
| Veggie burger | 1 patty | 13 |
| Chickpeas, cooked | 1 cup | 12 |
| Veggie baked beans | 1 cup | 12 |
| Pinto beans, cooked | 1 cup | 12 |
| Black-eyed peas, cooked | 1 cup | 11 |
| Tofu, firm | 4 ounces | 11 |
| Lima beans, cooked | 1 cup | 10 |
| Quinoa, cooked | 1 cup | 9 |
| Tofu, regular | 4 ounces | 9 |
| Bagel | 1 med (3 oz.) | 9 |
| Peas, cooked | 1 cup | 9 |
| Textured Vegetable Protein (TVP), cooked | 1/2 cup | 8 |
| Peanut butter | 2 Tbsp | 8 |
| Veggie dog | 1 link | 8 |
| Spaghetti, cooked | 1 cup | 8 |
| Almonds | 1/4 cup | 8 |
| Soy milk, commercial, plain | 1 cup | 7 |
| Soy yogurt, plain | 6 ounces | 6 |
| Bulgur, cooked | 1 cup | 6 |
| Sunflower seeds | 1/4 cup | 6 |
| Whole wheat bread | 2 slices | 5 |
| Cashews | 1/4 cup | 5 |
| Almond butter | 2 Tbsp | 5 |
| Brown rice, cooked | 1 cup | 5 |
| Spinach, cooked | 1 cup | 5 |
| Broccoli, cooked | 1 cup | 4 |
| Potato | 1 med (6 oz.) | 4 |








Facebook Comments