Do you need vitamin E supplement? First of all, let’s understand about “Vitamin E”. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble nutrient found in many foods. It acts as an antioxidant by helping to protect cells from the damage caused by free radicals.
The body also needs vitamin E to boost its immune system so that it can fight against bacteria and viruses. Vitamin E helps to widen blood vessels and keep blood from clotting within them.
Benefits of Vitamin E
- Balances cholesterol
- Fights against free radicals
- Repairs damaged skin
- Thickens hair
- Balances hormones
- Helps PMS symptoms
- Improves vision
How much Vitamin E Do You Need Daily?
Most adults need 15mg of vitamin E daily only. Breastfeeding women may need more than that, which is 19mg daily.
Sources of Vitamin E
The vitamin E molecules are naturally found in many foods and vegetables which we normally get enough in our diet without much worry.
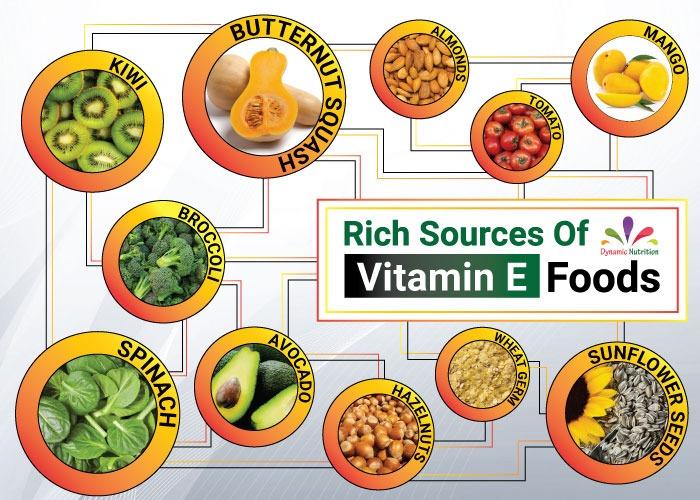
Rich sources of vitamin E foods:
- Sunflower seeds – 1 cup: 33.41 mg
- Almonds – 1 cup: 32.98 mg
- Hazelnuts – 1 cup: 20.29 mg
- Wheat Germ – 1 cup plain, uncooked: 18 mg
- Mango – 1 whole raw: 3.02 mg
- Avocado – 1 whole raw: 2.68 mg
- Butternut Squash – 1 cup cooked and cubed squash: 2.64 mg
- Broccoli – 1 cup cooked: 2.4 mg
- Spinach – ½ cup cooked: 1.9 mg
- Kiwi – 1 medium: 1.1 mg
- Tomato – 1 raw: 0.7 mg
Side Effects of Vitamin E
Vitamin E benefits most people when taken by mouth or applied directly to the skin. It may be unsafe when taken in very high amounts, especially for people who have conditions such as heart disease or diabetes.
Taking supplements with high levels of vitamin E could bring risk to:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Rash
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Problems with ovaries in females or testes in males
Risk Factor of Vitamin E Supplements
The risk factor of vitamin E supplements and foods fortified with vitamin E related to the fact that it may be derived from genetically modified (GM) plants. The chemical name for vitamin E is “tocopherol”. Tocopherol, which is the generic term for at least seven different types of vitamin E, are naturally formed in a variety of plants.
Tocopherol can be produced either by chemical synthesis or by extraction from:
- Maize
- Soybeans
- Cottonseed
- Rice
- Wheat germ oil
The so-called “natural” vitamin E, d-alpha tocopherol, is common in many other supplements. However, even though this vitamin E is a natural form, it is very unnatural for two reasons:
- It is in an isolated form without the rest of the naturally-occurring vitamin E complex. In nature, alpha-tocopherol exists with seven other vitamin E compounds: three other tocopherols and four tocotrienols.
- Supplements of alpha-tocopherol are usually very high, unnatural doses.
So, Do You Need Vitamin E Supplements?
Vitamin E is important for our body. We need vitamin E to help improve our immune system and prevent chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease. But we only need 15 mg per day which is more than enough. This is very easy to obtain from a diet, a tablespoon of vegetable oil is enough. This is the reason why almost no one is deficient in vitamin E.
Vitamin C Works Well With Vitamin E
Vitamin C works well with vitamin E because they have complementary roles in skin health. Both vitamins shield your skin cells from sun damage because they neutralize the free radicals generated during sun exposure. Vitamin C and E also work together to maintain healthy collagen. You need vitamin C to help synthesize the collagen required for healthy skin, and healthy vitamin E levels to maintain proper cross-links between collagen fibers.











Facebook Comments