
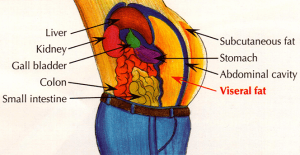
Visceral fat is technically excess intra-abdominal adipose tissue accumulation. It is known as a “deep” fat that is stored further underneath the skin than “subcutaneous” belly fat. It is a form of gel-like fat that is wrapped around internal organs, including the liver, pancreas, and kidneys. However, this fat is very close to the liver and can turn it into cholesterol. From there, the visceral fat goes through the bloodstream. It may collect along the walls of the arteries. This leads the arteries to get hard and narrow (called atherosclerosis). Too much of visceral fat creates can lead to inflammation and high blood pressure, which increases the risk of serious health problems as well. Visceral fat has been linked to metabolic disturbances and increased risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Another issue with visceral fat is its impact on adiponectin or “fat hormone”. Adiponectin is a special hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown. Visceral fat inhibits adiponectin. When adiponectin levels are low, the body can accumulate unhealthy fat and insulin resistance may take place.
Excess visceral fat is linked with an increased risk for:
- Heart disease
- Cancer
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Diabetes
- Depression
- Arthritis
- Obesity
- Sexual dysfunction
- Sleep disorders
What causes Visceral Fats?
When there is too much glucose in the bloodstreams and the cells are already filled glycogen stores, glucose is stored as fat. This happens a lot more quickly and easily when consuming refined processed carbohydrates and sugary foods. Processed starches like white bread or white rice, along with high-sugar foods, are rapidly converted into simple sugars that enter the bloodstream and trigger a larger release of insulin from the pancreas. The result is usually weight gain, some more even more hunger which leads to continuing overeating and a vicious cycle that makes it hard to stop eating sweets. Thus the more often and longer than blood insulin levels remain high, the more likely a person to accumulate excess body fat.
Related Topics
The Belly Visceral Fat – Blood Sugar Connection
How does Garcinia Cambogia Work on Weight Loss?
6 reasons for the formation of beer belly
Ashitaba Chalcones – Effective in fighting visceral fats
Calculate Your BMI – BMI calculator explained
Metabolic syndrome leads to cardiovascular diseases
Natural food to reduce belly fats #1 Oats
Here’s Exactly How Much You Should Walk Per Week to Burn Belly Fat — and See Results







Facebook Comments