When is the gastric pain not normal?
When an otherwise healthy person experiences pain, it’s like an alarm from the body that something is wrong. Abdominal pain that occurs as a result of self-limiting conditions like stomach flu (gastroenteritis) is not persistent. Gastric pain which is persistent, of increasing severity or unbearable, is not normal.

How to differentiate between gastric pain and stomach pain?
Abdominal pain is a symptom that could be representative of many diseases. There are different types of pain depending on the involved organ. The usually described cramps of gastroenteritis are gripping in nature with a waxing and waning character.
Gastric pain is usually located at the centre of the upper abdomen and varies in intensity, from a dull ache to a severe sharp cutting pain that is persistent. Since other organs are also located in the upper abdomen, it is difficult to use only pain as a marker.
Gastric pain has symptoms such as acid indigestion, heartburn, bloating or abdominal distension. The pain may vary from a dull ache to a severe, throbbing pain. Sometimes, gastric pain is associated with symptoms like vomiting and diarrhoea. During diagnostic tests, the symptoms will help to identify the underlying cause of gastric pain.
Organic causes of gastric pain
While gastric pain has no clear cause, doctors suspect a link with stress. In a minority of cases, tests can reveal the cause of the gastric pain to be one of the following:
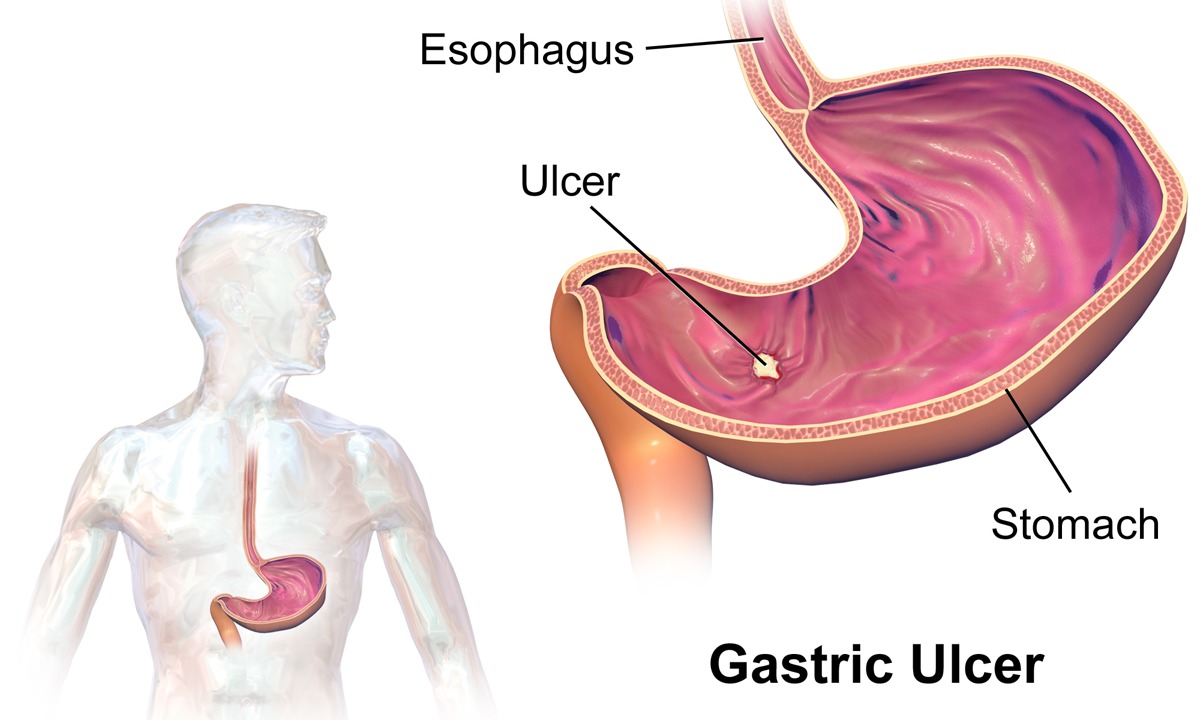
- Peptic ulcer disease: A defect in the innermost layer of the stomach or duodenum wall (where the small intestine connects to the stomach).Most peptic ulcers are due to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, as well as to the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and other painkillers.H. pylori infection can be ruled out by a blood test, urea breath test, stool test or by tests done during endoscopy.
- Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD): A chronic condition where stomach acid or bile flows back into your food pipe (oesophagus), irritating its lining.To rule out GERD, your doctor may recommend an endoscopy. In this exam, a thin tube containing a tiny camera is passed through the mouth to examine the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Gallstone disease: Gallstones usually do not cause any signs or symptoms. However, inflammation of the gallbladder or blockage of the bile duct may lead to severe abdomen pain. Occasionally, gallstones on their own may cause pain without significant inflammation of the gallbladder or blockage of the bile duct.Ultrasound scans and CT scans can help to reveal the presence of gallstones.
5 Best Home Remedies for Gastritis
1. Follow an anti-inflammatory diet
Gastritis refers to inflammation of the stomach lining, so consuming a diet that helps to minimize inflammation may provide relief over time. However, research has not conclusively shown that eating a certain diet causes or prevents gastritis.
By keeping a food diary, people can identify which foods trigger their symptoms. They can then begin to reduce their intake or avoid certain foods altogether.
Foods that commonly contribute to inflammation are:
- processed foods
- gluten
- acidic foods
- dairy products
- sugary foods
- spicy foods
- alcohol
2. Try probiotics
Probiotics can help improve digestion and encourage regular bowel movements. Probiotic supplements introduce good bacteria into a person’s digestive tract, which may help stop the spread of H. pylori.
 Eating foods that contain probiotics may also improve the symptoms of gastritis. These foods include:
Eating foods that contain probiotics may also improve the symptoms of gastritis. These foods include:
- yoghurt
- kimchi
- kombucha
- sauerkraut
- kefir
3. Eat lighter meals
Eating large, carbohydrate-heavy meals can put a strain on a person’s digestive system and aggravate gastritis.
Eating small meals regularly over the course of the day can help ease the digestive process and reduce the symptoms of gastritis.
4. Avoid smoking and overuse of painkillers
Smoking can damage a person’s stomach lining and also increases a person’s risk of developing stomach cancer.
Taking too many over-the-counter pain medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, can also damage the stomach lining and make gastritis worse.
5. Reduce stress
Stress can cause gastritis flare-ups, so reducing stress levels is an important way to help manage the condition.
Stress management techniques include:
- massage
- meditation
- yoga
- breathing exercises







Facebook Comments