When most people think of enzymes, they think of digestive health. While your body has over 75,000 enzymes, only a handful deal with digestion. Meanwhile, the rest help your body use vital nutrients to work properly and stay healthy.
So what exactly are metabolic enzymes?
Enzymes are biologically active proteins found in all living cells. Metabolic enzymes catalyze and regulate every biochemical reaction that occurs within the human body, making them essential for cellular function and overall health. Digestive enzymes turn the food we eat into energy which may be utilized by the body for various biological processes. Our bodies naturally produce both digestive and metabolic enzymes, as they are needed.
Metabolic Enzymes are an essential component for optimal cellular function and health. These descriptions are not without merit. They speed up the chemical reactions within the cells for detoxification and energy production. They enable us to see, hear, feel, move and think. Every organ, every tissue and all 100 trillion cells in our body depend upon the reaction of metabolic enzymes and their energy factor. Without these metabolic enzymes, cellular life would cease to exist.
Metabolic enzymes are also known has “liver enzymes”
Liver enzymes are often referred to as metabolic enzymes which are in your body and make everything ‘work’. There may be millions of different types because a different enzymes because each has a different job.
Metabolic enzymes are different than digestive enzymes (which digest or breakdown organic matter – we call it ‘food’). When digestive enzyme action breaks down organic matter in our bodies, we call it ‘eating food’. These two categories of enzymes are not interchangeable.
Metabolic enzymes are totally different from digestive enzymes. They are produced exclusively by the liver to help all cells, organs, glands and blood attain peak functioning. Metabolic enzymes carry out a variety of cellular functions necessary for survival like digestion, cellular respiration, energy storage, transcription, response to the environment.
How does metabolic enzymes work?
A cell’s daily operations are accomplished through the biochemical reactions that take place within the cell. Reactions are turned on and off or sped up and slowed down according to the cell’s immediate needs and overall functions. At any given time, the numerous pathways involved in building up and breaking down cellular components must be monitored and balanced in a coordinated fashion. To achieve this goal, cells organize reactions into various enzyme-powered pathways or metabolic pathways
Metabolic enzymes can be involved at every step in a metabolic reaction pathway. Cells must balance their metabolic pathways in order to ensure that sufficient energy is available. This is critical for maintaining the normal function of an organ.
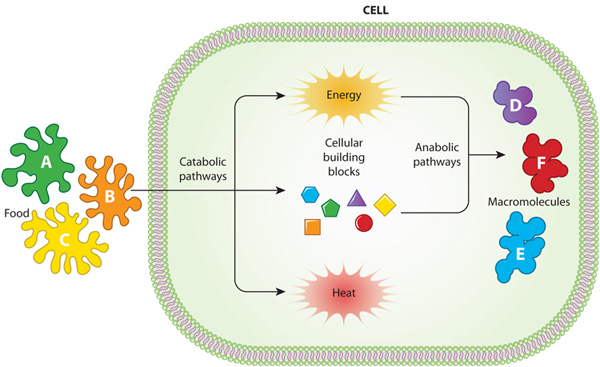
The role of metabolic enzymes is an important part of cellular maintenance. Enzymatic activity allows a cell to respond to changing environmental demands and regulate its metabolic pathways, both of which are essential to cell survival.
What will happen if I have low metabolic enzymes?
A reduced amount of metabolic enzymes and aging go hand in hand because the enzymes are required to maintain a strong and healthy body. Naturally, the production of enzymes slows down with age, which makes it even more important for you to increase the levels whenever possible. Once the body begins to lack those enzymes, many age-related and degenerative diseases begin to develop.
How do I increase metabolic enzymes?
Two of the best ways to increase metabolic enzymes are with raw foods and a moderate amount of exercise. Enzyme supplements can also help to increase the enzyme levels; however, they might not be as effective as raw foods. Bananas, papayas, and pineapples are rich with enzymes that can help to increase the levels naturally. As with many other substances, the production of enzymes decreases with age.
A moderate amount of exercise can help with the production of these enzymes as well. Exercise helps the body to increase in muscle mass and speeds up the metabolism. Nevertheless, it is important to keep the exercise within moderate levels as intense or prolonged exercise sessions seem to have the opposite effect. The key is to listen to your body and stop when it begins to tire.
Many enzyme supplements can also help; however, not all supplements have the same levels of activity and effectiveness. The higher the activity and effectiveness, the more beneficial they are in helping increase the enzymes.







Facebook Comments